Third Maori War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century
The Invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century

 Cameron, a
Cameron, a
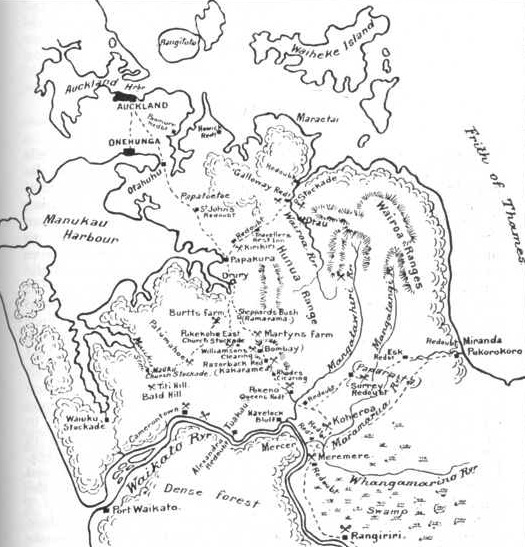 Three weeks later, on 20 November, Cameron, commanding a battle force of more than 1400 men, launched an attack on Rangiriri, further up the Waikato River. The battle cost both sides more than any other engagement of the land wars and also resulted in the capture of 180 Māori combatants, which impacted on their subsequent ability to oppose the far bigger British force.
The Rangiriri line, engineered by Te Wharepu, a leading Waikato chief, was a one kilometre-long system of deep trenches and high parapets that ran between the Waikato River and
Three weeks later, on 20 November, Cameron, commanding a battle force of more than 1400 men, launched an attack on Rangiriri, further up the Waikato River. The battle cost both sides more than any other engagement of the land wars and also resulted in the capture of 180 Māori combatants, which impacted on their subsequent ability to oppose the far bigger British force.
The Rangiriri line, engineered by Te Wharepu, a leading Waikato chief, was a one kilometre-long system of deep trenches and high parapets that ran between the Waikato River and
 Construction of a new and even more formidable defence line began 25 km south of Ngāruawāhia, soon after the fall of Rangiriri. The line included fortifications at Pikopiko and Rangiatea and was centered on
Construction of a new and even more formidable defence line began 25 km south of Ngāruawāhia, soon after the fall of Rangiriri. The line included fortifications at Pikopiko and Rangiatea and was centered on
 Following the fall of the Paterangi line, Wiremu Tamihana, leading one of the two major Kingite divisions, retreated east to Maungatautari to block a British advance up the Waikato River into Ngati Raukawa territory and
Following the fall of the Paterangi line, Wiremu Tamihana, leading one of the two major Kingite divisions, retreated east to Maungatautari to block a British advance up the Waikato River into Ngati Raukawa territory and
 Another ''runanga'' was held before dawn on 2 April and again Tupotahi urged them to break out. Though many of the chiefs remained steadfast in their refusal to retreat, Rewi insisted the effect of the water shortage was now so severe they had to break out, but urged they go out fighting. The plan was aborted when dawn broke and the fog lifted, removing their cover. Through the morning the British sap advanced close enough to the outer trenches of Ōrākau for hand-grenades to be thrown over the ramparts. At noon Cameron arrived with more men, bringing the besieging imperial and colonial force to 1800. One of the Armstrong guns was moved to the head of the sap and fired at the
Another ''runanga'' was held before dawn on 2 April and again Tupotahi urged them to break out. Though many of the chiefs remained steadfast in their refusal to retreat, Rewi insisted the effect of the water shortage was now so severe they had to break out, but urged they go out fighting. The plan was aborted when dawn broke and the fog lifted, removing their cover. Through the morning the British sap advanced close enough to the outer trenches of Ōrākau for hand-grenades to be thrown over the ramparts. At noon Cameron arrived with more men, bringing the besieging imperial and colonial force to 1800. One of the Armstrong guns was moved to the head of the sap and fired at the
Waikato Raupatu Claims Settlements Act 1995, Parliamentary Counsel Office, NZ Legislation
/ref> Queen
War in the Waikato
(NZHistory) {{DEFAULTSORT:Invasion Of Waikato Conflicts in 1863 Conflicts in 1864 New Zealand Wars 1863 in New Zealand 1864 in New Zealand History of Waikato
 The Invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century
The Invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century New Zealand Wars
The New Zealand Wars took place from 1845 to 1872 between the New Zealand colonial government and allied Māori on one side and Māori and Māori-allied settlers on the other. They were previously commonly referred to as the Land Wars or the M ...
. Hostilities took place in the North Island
The North Island, also officially named Te Ika-a-Māui, is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but much less populous South Island by the Cook Strait. The island's area is , making it the world's 14th-largest ...
of New Zealand between the military forces of the colonial government and a federation of Māori tribes known as the Kingitanga Movement. The Waikato
Waikato () is a Regions of New Zealand, local government region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipa District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton City ...
is a territorial region with a northern boundary somewhat south of the present-day city of Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
. The campaign lasted for nine months, from July 1863 to April 1864. The invasion was aimed at crushing Kingite power (which European settlers saw as a threat to colonial authority) and also at driving Waikato Māori from their territory in readiness for occupation and settlement by European colonists.
The campaign was fought by a peak of about 14,000 Imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texa ...
and colonial troops and about 4,000 Māori warriors drawn from more than half the major North Island tribal groups.
Plans for the invasion were drawn up at the close of the First Taranaki War
The First Taranaki War (also known as the North Taranaki War) was an armed conflict over land ownership and sovereignty that took place between Māori people, Māori and the New Zealand government in the Taranaki district of New Zealand's North ...
in 1861 but the Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of col ...
and New Zealand General Assembly opposed action, and the incoming Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Sir George Grey
Sir George Grey, KCB (14 April 1812 – 19 September 1898) was a British soldier, explorer, colonial administrator and writer. He served in a succession of governing positions: Governor of South Australia, twice Governor of New Zealand, Go ...
(second term 1861–1868) suspended execution in December of that year. Grey reactivated the invasion plans in June 1863 amid mounting tension between Kingites and the colonial government and fears of a violent raid on Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
by Kingite Māori. Grey used as the trigger for the invasion Kingite rejection of his ultimatum on 9 July 1863 that all Māori living between Auckland and the Waikato take an oath of allegiance to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
or be expelled south of the Waikato River
The Waikato River is the longest river in New Zealand, running for through the North Island. It rises on the eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu, joining the Tongariro River system and flowing through Lake Taupō, New Zealand's largest lake. It th ...
. Government troops crossed into Waikato territory three days later and launched their first attack on 17 July at Koheroa, but were unable to advance for another 14 weeks.
The subsequent war included the Battle of Rangiriri
The Battle of Rangiriri was a major engagement in the invasion of Waikato, which took place on 20–21 November 1863 during the New Zealand Wars. More than 1400 British troops defeated about 500 warriors of the Kingitanga (Māori King Movement), ...
(November 1863)—which cost both sides more men than any other engagement of the New Zealand Wars—and the three-day-long Battle of Ōrākau
The Invasion of the Waikato became the largest and most important campaign of the 19th-century New Zealand Wars. Hostilities took place in the North Island of New Zealand between the military forces of the Colony of New Zealand, colonial gover ...
(March–April 1864), which became arguably the best-known engagement of the New Zealand Wars and which inspired two films called ''Rewi's Last Stand
''Rewi's Last Stand'' is the title of two feature films directed by pioneering New Zealand filmmaker Rudall Hayward: a 1925 silent movie, and 1940 remake with sound. They are historical dramas, based on the last stand of Rewi Maniapoto at the B ...
''. The campaign ended with the retreat of the Kingitanga Māori into the rugged interior of the North Island and the colonial government confiscating about 12,000 km2 of Māori land.
The defeat and confiscations left the King Movement tribes with a legacy of poverty and bitterness that was partly assuaged in 1995 when the government conceded that the 1863 invasion and confiscation was wrongful and apologised for its actions. The Waikato–Tainui tribe accepted compensation in the form of cash and some government-controlled lands totalling about $171 million—about 1 percent of the value of the lands confiscated in 1863—and later that year Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
personally signed the Waikato Raupatu Claims Settlement Act 1995
The Waikato Raupatu Claims Settlement Act 1995 is an act of the New Zealand Parliament passed into law in 1995. It was the first act implementing a major historical Treaty of Waitangi settlement since the Treaty of Waitangi Act 1975 was amended ...
.
(The Governor-General normally gives Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in other ...
to legislation by signing on the monarch's behalf.)
Background and origins of the invasion
TheFirst Taranaki War
The First Taranaki War (also known as the North Taranaki War) was an armed conflict over land ownership and sovereignty that took place between Māori people, Māori and the New Zealand government in the Taranaki district of New Zealand's North ...
had ended in March 1861 as an uneasy truce between the government and Māori forces, with both sides recognising they had reached a stalemate. The lack of a clear victory by imperial forces led Governor Thomas Gore Browne
Colonel Sir Thomas Robert Gore Browne, (3 July 1807 – 17 April 1887) was a British colonial administrator, who was Governor of St Helena, Governor of New Zealand, Governor of Tasmania and Governor of Bermuda.
Early life
Browne was born on ...
to turn his attention to the Waikato, the centre of the Kingite movement, where king Tāwhiao
Tāwhiao (Tūkāroto Matutaera Pōtatau Te Wherowhero Tāwhiao; c. 1822 – 26 August 1894) was leader of the Waikato tribes, the second Māori King, and a religious figure. He was a member of the Ngati Mahuta (Hapū) of Waikato.
Biography
T ...
was attracting the allegiance of increasing numbers of Māori across the North Island. Browne concluded that members of the Kingite movement would have to be compelled to submit to British rule. After attempting to achieve a peace settlement through "kingmaker
A kingmaker is a person or group that has great influence on a royal or political succession, without themselves being a viable candidate. Kingmakers may use political, monetary, religious and military means to influence the succession. Origina ...
" Wiremu Tamihana
Wiremu Tamihana Tarapipipi Te Waharoa ( – 27 December 1866), generally known as Wiremu Tamihana, was a leader of the Ngāti Hauā Māori iwi in nineteenth century New Zealand, and is sometimes known as the kingmaker for his role in the Māori Kin ...
, in mid-1861 he sent an ultimatum to the movement's leaders, demanding submission to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
and the return of plunder taken from Taranaki; when it was rejected he began drawing up plans to invade the Waikato and depose the king—a plan opposed by both the Colonial Office
The Colonial Office was a government department of the Kingdom of Great Britain and later of the United Kingdom, first created to deal with the colonial affairs of British North America but required also to oversee the increasing number of col ...
and the New Zealand General Assembly. According to Browne, in response to his belligerence, Kingite leaders formed plans to launch a raid on Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
on 1 September and burn the town and slaughter most of its residents. This has since been dismissed by such historians as James Belich as being fear-mongering from Browne in order to try and gain military support.
Browne's invasion plan was suspended when he was replaced by Sir George Grey
Sir George Grey, KCB (14 April 1812 – 19 September 1898) was a British soldier, explorer, colonial administrator and writer. He served in a succession of governing positions: Governor of South Australia, twice Governor of New Zealand, Go ...
in September that year, and the Kingites in turn abandoned their plan for their uprising. Grey instead instituted a peace policy that included a system of Māori local administration in which they could participate, hoping it would encourage Māori to abandon the Kingite movement and "reduce the number of our enemies". At the same time, however, Grey began planning for war, using troops from the newly formed Commissariat Transport Corps to start construction work on a road from Drury that would run about 18 km south through forest to the Kingite border at the Mangatawhiri Stream—a tributary of the Waikato River—near Pokeno. The so-called Great South Road would provide quick access to troops in the event of an invasion. Using what historian James Belich describes as a campaign of misinformation, Grey retained the Taranaki army and began appealing to the colonial office for more troops to avert "some great disaster", claiming tensions remained high, with a high likelihood of Māori aggression. In November 1862 he ordered a gunboat steamer from Sydney and purchased another in Lyttelton to supplement the supply system. By early 1863 the imperial government had provided Grey with 3000 men for the expected war.
Events in early 1863 brought tensions to a head. In March Kingites obstructed the construction of a police station at Te Kohekohe, near Meremere
Meremere is a small town in the northern Waikato region in the North Island of New Zealand. It is located on the east bank of the Waikato River, 50 kilometres north of Hamilton and 63 km south of Auckland.
Meremere was the site of fighting ...
, and 80 armed warriors raided the 80 hectare property at Te Awamutu
Te Awamutu is a town in the Waikato region in the North Island of New Zealand. It is the council seat of the Waipa District and serves as a service town for the farming communities which surround it. Te Awamutu is located some south of Hamilto ...
occupied by magistrate and Commissioner John Gorst, seizing the printing press on which he published a newspaper and taking it to Kihikihi. The raiders, led by Rewi Maniapoto
Rewi Manga Maniapoto (1807–1894) was a Ngāti Maniapoto chief who led Kīngitanga forces during the New Zealand government Invasion of Waikato during the New Zealand Wars.
Kinship
Rewi, or Manga as he was known to his kin, was the child of ...
and Wiremu Kīngi
Wiremu Kīngi Te Rangitāke (c. 1795 – 13 January 1882), Māori Chief of the Te Āti Awa Tribe, was leader of the Māori forces in the First Taranaki War.
He was born in 1795-1800 in Manukorihi pa, near Waitara. He was one of the 3 sons of ...
, sent a message to Gorst—who was absent at the time—to quit the property or risk death; Grey recalled Gorst to Auckland soon after. On 4 April Grey arranged for a 300-strong Imperial force to evict Māori from the contested Tataramaika block in Taranaki
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the city of New Plymouth. The New Plymouth Dist ...
and reoccupy it. Māori viewed the reoccupation as an act of war and on 4 May a party of about 40 Ngati Ruanui warriors carried out a revenge attack, ambushing a small military party on a coastal road at nearby Oakura, killing all but one of the 10 soldiers. The ambush, ordered by Rewi, may have been planned as an assassination attempt on Grey, who regularly rode the track between New Plymouth and the Tataraimaka military post.
Imperial troops were moved back to Taranaki as hostilities resumed and on 4 June the new British commander, Lieutenant-General Duncan Cameron, led 870 troops to attack a party of about 50 Māori on the Tataraimaka block, killing 24. Concerned by the renewed aggression, some Kingites began resurrecting their plan to raid Auckland and its frontier settlements. The colonial ministry remained unconvinced Auckland or Wellington were in any danger and had refused to call out the Auckland militia following the Oakura ambush, and missionaries and even Gorst dismissed the likelihood of an attack. But in correspondence to London Grey cited that incident as further proof of the imminent danger to New Zealand settlers.
On 9 July 1863 Grey issued a new ultimatum, ordering that all Māori living between Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
and the Waikato take an oath of allegiance to Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
or be expelled south of the river. As many young men retreated into the bush with their weapons, officials began seizing others—including the ill and aged—who declined to swear the oath, imprisoning them without charge. Two days later Grey issued a proclamation directed to the "Chiefs of Waikato", which read:
Within a day—before the proclamation had even reached the Waikato—Grey ordered the invasion of the Kingite territory, claiming he was making a punitive expedition against Rewi over the Oakura ambush and a pre-emptive strike to thwart a "determined and bloodthirsty" plot to attack Auckland. Though Grey claimed it was a defensive action, historian B. J. Dalton claimed his reports to London had been "a deliberate and transparent falsehood" and that the invasion was an act of "calculated aggression". On 12 July Duncan Cameron and the first echelon of the invading army crossed the Mangatawhiri Stream.
First engagements

 Cameron, a
Cameron, a Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
veteran who had replaced Major-General Thomas Pratt as commander-in-chief of the British troops, began the invasion with fewer than 4000 effective troops in Auckland at his disposal. But the continuous arrival of regiments from overseas rapidly swelled the force. (Total troop numbers reached 10,000 in January 1864 before peaking at about 14,000 in March 1864—9000 imperial troops, more than 4000 colonial and a few hundred '' kūpapa'', or pro-British Māori.)
Cameron's initial invasion force set up camp on the site of an old '' pā'' on a hill above the stream. Reinforcements continued to arrive and within days he had 500 troops. On the morning of 17 July Cameron led 553 men on a raid on a new and unfinished entrenchment at Koheroa, near Mercer. Cameron ran ahead of his force after they took early fire from Māori outposts and the Māori fighters fled. According to Belich, the Māori force numbered between 100 and 150 and about 15 were killed, some of them by bayonet. Among the dead were their leader Te Huirama, a relative of King Tāwhiao. British casualties totalled one dead and 12 wounded. But the same day a Māori war party ambushed a convoy of six carts and its 50-man escort well behind British lines, at Martin's Farm near Ramarama on the Great South Road. A third of the British force were cut down—five soldiers killed and 11 wounded—while Māori losses were limited to two. The attack prompted the establishment of five new redoubts on the route, taking 510 of Cameron's men.
The bush raid was the beginning of a new Māori strategy that would drain Cameron's resources and halt his advance for another 14 weeks. On 22 July a group of about 40 Māori fatally shot a settler cutting timber at Pukekiwiriki near Papakura and were pursued into the forest by the Auckland militia. Seven Māori were killed. When two more settlers were killed at isolated farms near Drury on 24 July, the government formed a special corps of bush fighters named the "Forest Rangers", who began a series of bush reconnaissance missions and pursuits of armed Māori bands. Cameron wrote: "The bush is now so infested with these natives that I have been obliged to establish strong posts along our line of communication, which absorbs so large a portion of the force that until I receive reinforcements it is impossible for me to advance further up the Waikato."
By the end of August Cameron's forces had grown to 6000 effectives. He had the armoured 40-ton paddle-steamer ''Avon''—20m long, drawing one metre of water and armed with a 12-pounder Armstrong in the bows—as well as boats, barges and canoes. But Māori defences had also grown: the so-called Meremere Line—a 22 km-long line of fortifications that spread from Pukekawa
Pukekawa is a town in the Lower Waikato River area of New Zealand's North Island, 66 km south of central Auckland. The area's fertile soils are used to grow a range of vegetables, including onions, potatoes and carrots. The town was in ...
to Meremere and Paparata—had been built, commanding about 2000 square kilometres of bush and manned by a force of up to 1500. The Meremere Line allowed bands of between 20 and 200 Māori warriors to freely cross the Waikato River and harass troops and kill settlers towards Auckland. On 25 August a party of Māori snatched up the rifles and ammunition from a group of 25 soldiers who were timber-felling beside the Great South Road—part of an effort to destroy cover for Māori raiders intent on mounting further ambushes—and killed two soldiers. On 2 September a British party of 62 men was fired on from the rear during a march on the village of Pokeno, but managed to pursue their attackers and inflict some casualties.
In mid-August the British established an alternative supply line to the Great South Road, using a combination of steamers from Onehunga
Onehunga is a suburb of Auckland in New Zealand and the location of the Port of Onehunga, the city's small port on the Manukau Harbour. It is south of the Auckland CBD, city centre, close to the volcano, volcanic cone of Maungakiekie / One Tree ...
to the Waikato Heads and canoes paddled up the Waikato by friendly Māori to Queen's Redoubt at Pokeno. But on 7 September a Ngāti Maniapoto
Ngāti Maniapoto is an iwi (tribe) based in the Waikato-Waitomo region of New Zealand's North Island. It is part of the Tainui confederation, the members of which trace their whakapapa (genealogy) back to people who arrived in New Zealand on the ...
war party launched an attack on that supply line, killing resident magistrate James Armitage—who was supervising a shipment of stores—and burning a stores depot with 40 tons of supplies at Camerontown Camerontown or Cameron Town was a British Army supply depot used during the Invasion of the Waikato during the New Zealand Wars in 1863, and later a small settlement.
Location
The depot was on the north bank of the lower Waikato River, west of Tu ...
on the north bank of the Waikato River near Tuakau. The Ngāti Maniapoto then attacked a British redoubt overlooking Pokeno, from which they were driven off. The attack on the supply line, said Belich, "was easily the most important single action of the first phase of the war".
Cameron responded by creating a series of about 20 stockades and redoubts all over the district, designed to protect the supply line and impede the ability of Māori to attack further north. Each stockade needed its own garrison—from 25 to 55 men—and supply line, eventually accounting for almost 6000 of his men, further draining him of frontline manpower. But Māori raids continued: almost 200 Ngāti Maniapoto surrounded a militia stockade at a Pukekohe East
Pukekohe is a town in the Auckland Region of the North Island of New Zealand. Located at the southern edge of the Auckland Region, it is in South Auckland, between the southern shore of the Manukau Harbour and the mouth of the Waikato River. ...
church on 14 September, losing about 40 men, and the same day a 20-man Ngāti Pou force attacked a homestead at Paerata, midway between Pukekohe and Drury, but were driven off by neighbours. The turning point for Cameron came in late October when hundreds of Waikato militia replaced regulars at the outposts, another 500 imperial troops arrived from Australia—now giving him a striking force of almost 2000 and a total of 8000 effectives—and a second river steamer, HMS ''Curacoa'', was brought to the front. On 31 October a river flotilla including ''Avon'', the gunboats ''Curacoa'' and ''Pioneer'' and armoured barges steamed past Meremere—drawing fire from rifle pits and batteries of ships guns, some of them firing pieces of iron chain and pound weights—and landed 600 men at Takapau, 15 km upriver, ready to attack the heart of the defensive line from the rear. The flotilla returned downstream, intending to bring up another 600 men the next day for the attack, but the plan was dropped when the Māori force evacuated the Meremere fortifications the following day and escaped eastwards across flooded lagoons by canoe, falling back to their next defensive system at Rangiriri.
Rangiriri
 Three weeks later, on 20 November, Cameron, commanding a battle force of more than 1400 men, launched an attack on Rangiriri, further up the Waikato River. The battle cost both sides more than any other engagement of the land wars and also resulted in the capture of 180 Māori combatants, which impacted on their subsequent ability to oppose the far bigger British force.
The Rangiriri line, engineered by Te Wharepu, a leading Waikato chief, was a one kilometre-long system of deep trenches and high parapets that ran between the Waikato River and
Three weeks later, on 20 November, Cameron, commanding a battle force of more than 1400 men, launched an attack on Rangiriri, further up the Waikato River. The battle cost both sides more than any other engagement of the land wars and also resulted in the capture of 180 Māori combatants, which impacted on their subsequent ability to oppose the far bigger British force.
The Rangiriri line, engineered by Te Wharepu, a leading Waikato chief, was a one kilometre-long system of deep trenches and high parapets that ran between the Waikato River and Lake Waikare
Lake Waikare is the largest of several shallow lakes in the upper floodplain of the Waikato River in New Zealand's North Island. It is a riverine lake, located to the east of Te Kauwhata and 40 kilometres north of Hamilton. It covers .
Due to it ...
. The front line ran east–west, while another line of defences ran south from the main line, facing the river. In the centre of the main line lay a small but well-protected north-facing redoubt
A redoubt (historically redout) is a fort or fort system usually consisting of an enclosed defensive emplacement outside a larger fort, usually relying on earthworks, although some are constructed of stone or brick. It is meant to protect soldi ...
with several lines of concealed rifle pits at its southern side. The defences consisted solely of earthworks, with no palisading; a redoubt midway along the main line, had a low profile and was deceptively strong.
Cameron arrived at Rangiriri with about 850 men, chiefly of the 65th, 14th
14 (fourteen) is a natural number following 13 (number), 13 and preceding 15 (number), 15.
In relation to the word "four" (4), 14 is spelled "fourteen".
In mathematics
* 14 is a composite number.
* 14 is a square pyramidal number.
* 14 is a s ...
and 12th
12 (twelve) is the natural number following 11 and preceding 13. Twelve is a superior highly composite number, divisible by 2, 3, 4, and 6.
It is the number of years required for an orbital period of Jupiter. It is central to many systems ...
regiments, to make the frontal assault. A second division of 320 men of the 40th Regiment under Lieut-Colonel Arthur Leslie with additional naval backup, were transported by barge further south with the aim of gaining possession of a ridge 500 metres behind the main entrenchment and cutting off any escape. The assault force, armed with three Armstrong guns, revolvers, Enfield rifles with fixed bayonet
A bayonet (from French ) is a knife, dagger, sword, or spike-shaped weapon designed to fit on the end of the muzzle of a rifle, musket or similar firearm, allowing it to be used as a spear-like weapon.Brayley, Martin, ''Bayonets: An Illustr ...
s and hand grenade
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade genera ...
s, faced a Māori force of about 500 men, mostly armed with double-barreled shotgun
A double-barreled shotgun is a break-action shotgun with two parallel barrels, allowing two single shots to be fired in quick succession or simultaneously.
Construction
Modern double-barreled shotguns, often known as ''doubles'', are almost u ...
s and musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually d ...
s.
About 3pm Cameron launched a two-hour bombardment from artillery and gunboats. Without waiting for Leslie's division, which was delayed by adverse conditions on the river, he began his frontal attack, storming the Māori positions across a 600m gap under heavy fire and immediately suffering casualties. Members of the 12th and 14th regiments who tried to climb the earthworks near the centre of the line with the aid of ladders were shot down and within a short time 40 of the British were dead or wounded. Members of the 65th Regiment, however, were more successful in reaching the trenches at the river side of the fortification, bridging them with planks and penetrating the Māori line. They killed about 30 Māori, with the surviving defenders fleeing south or towards the main redoubt. But when Cameron ordered an attack on the redoubt from the river side, his men began to come under heavy fire. Cameron ordered two more unsuccessful assaults on the central redoubt, which lifted British casualties to about 110.
As night fell, the British, dispirited by the scale of losses, slept on the wet ground, ready to renew the combat in the morning. But about 5am the Rangiriri garrison—still with arms and ammunition and with an escape route open to the east—raised a white flag, expecting to talk terms with Cameron. British soldiers advanced on the redoubt and entered, shook hands with their combatants, then surprised the Māori by demanding they surrender all their arms and taking them prisoner.
Belich wrote: "The capture of Rangiriri was not the result of assault or encirclement, but of the British misuse of a flag of truce. The Māoris might conceivably have eventually decided to surrender unconditionally anyway, but they might also have repelled further assaults and escaped across the lake." He said they might have also been gaining time waiting for reinforcements who were almost on the scene. About 35 of the Māori force were killed, along with six women and children. Probably an equal number of injured were evacuated by canoe across Lake Waikare. With the capture of more than 180 warriors, the battle became the most costly Māori defeat in the Waikato wars. The 183 prisoners were held without trial on an old coal hulk in Waitematā Harbour
Waitematā Harbour is the main access by sea to Auckland, New Zealand. For this reason it is often referred to as Auckland Harbour, despite the fact that it is one of two harbours adjoining the city. The harbour forms the northern and easter ...
before being moved to Kawau Island
Kawau Island is in the Hauraki Gulf / Tīkapa Moana, close to the north-eastern coast of the North Island of New Zealand. At its closest point it lies off the coast of the Northland Peninsula, just south of Tāwharanui Peninsula, and about ...
, north of Auckland, but in September 1864 they escaped and eventually made their way back to the Waikato.
Cameron attracted both praise for his "skilful measures" in the capture of Rangiriri and severe criticism over the high number of British losses. Yet the battle had highlighted the rapidly growing disparity between British and Māori forces and the inability of Waikato Māori to maintain their manpower continuously. Several Waikato chiefs including Te Wharepu expressed a willingness to negotiate and on 8 December the Kingite capital at Ngāruawāhia
Ngāruawāhia () is a town in the Waikato region of the North Island of New Zealand. It is located north-west of Hamilton at the confluence of the Waikato and Waipā Rivers, adjacent to the Hakarimata Range. Ngāruawāhia is in the Hamilton Ur ...
was abandoned and then taken by Cameron's troops. But Māori were still opposed to the British demands of submitting to the Queen and surrendering all arms and lands and began building further defences south of Ngāruawāhia.
Pāterangi and Rangiaowhia
 Construction of a new and even more formidable defence line began 25 km south of Ngāruawāhia, soon after the fall of Rangiriri. The line included fortifications at Pikopiko and Rangiatea and was centered on
Construction of a new and even more formidable defence line began 25 km south of Ngāruawāhia, soon after the fall of Rangiriri. The line included fortifications at Pikopiko and Rangiatea and was centered on Paterangi
Paterangi is a settlement in the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It is located 10 km northwest of Te Awamutu. It is close to the site of one of the most strongly fortified pa built during the New Zealand wars of the late 19th ...
, its largest ''pā'', and was designed to block the main approaches to the agriculturally rich Rangiaowhia
Rangiaowhia (or Rangiawhia, or Rangiaohia) was, for over 20 years, a thriving village on a ridge between two streams in the Waikato region, about east of Te Awamutu. From 1841 it was the site of a very productive Māori mission station until the ...
district, east of Te Awamutu
Te Awamutu is a town in the Waikato region in the North Island of New Zealand. It is the council seat of the Waipa District and serves as a service town for the farming communities which surround it. Te Awamutu is located some south of Hamilto ...
, a major economic base, trading with Auckland, San Francisco and Melbourne, and a supply centre of the Kingite tribes. By the end of January 1864 the line had become the largest system of Māori fortifications of the land wars, consisting of at least four large ''pā'' spaced about 8 km apart, each of which included complex sets of entrenchments and parapets. The defence system, which included two cannons, was manned by a force of between 1200 and 2000 men from a dozen major Waikato ''iwi''.
Two weeks after capturing Ngāruawāhia, Cameron's 3000-strong striking force, protected by another 4000 men, began slowly and cautiously advancing south. In late January Cameron moved his army headquarters to Te Rore
Te Rore was in the 1850s an important transhipment point on New Zealand's Waipā River, between the Rangiaowhia#Crops, agriculture of the Waikato basin and its Auckland market. That was ended in 1864 by the Invasion of the Waikato, when Te Rore was ...
, about 5 km from Paterangi, with an advance camp for 600 men positioned just 1.2 km from the ''pā'', from where they judged the defences were "immensely strong". Cameron, whose men continued to be targeted daily by sniper fire and attacks on short reconnaissance missions, decided that rather than a frontal attack, the more prudent approach would be to outflank the Paterangi line. He gained the help of two Māori guides, Himi Manuao (James Edwards) and John Gage, who had previously lived in the area, who revealed a route that bypassed it to the west and south to reach Te Awamutu. A new supply line was established from Auckland, using boats to Raglan and packhorses across the ranges to meet steamers on the Waipā River
The Waipā River is in the Waikato region of the North Island of New Zealand. The headwaters are in the Rangitoto Range east of Te Kuiti. It flows north for , passing through Ōtorohanga and Pirongia, before flowing into the Waikato River at ...
. But a further advance into the heart of Kingitanga territory was delayed when the ''Avon''—one of the most important components of the transport and supply system—accidentally sank in the Waipa on 8 February.
A significant engagement took place on 11 February when an assault party from Paterangi ambushed a group of soldiers bathing in a loop of the Mangapiki Stream at Waiari, near the British forward position. Two hundred of Cameron's troops, with the Forest Rangers, became involved in a running battle with the attackers and killed an estimated 41 Māori, losing six of their own men.
Bishop George Selwyn, as garrison chaplain, had been told on 12 February that women, children and elderly would be taking refuge at unfortified and undefended Rangiaowhai, and had been asked to communicate that with Cameron. Kingitanga leaders understood they would be unharmed. There were about 200 Ngati-Apakura and Ngati-Hinetu people at Rangiaowhia, supplying food to the garrisons at Paterangi ''pā''.
Cameron, meanwhile, was attracting sharp criticism from both the colonist press and Grey himself about the lack of progress in the eight weeks since Ngāruawāhia's capture. On the night of 20 February, he set out on the narrow bush track to bypass Paterangi with 1230 men led by one of his guides and the Forest Rangers, leaving a large masking force in front of Paterangi. The force marched through rough bush in silence and complete darkness, passing within 1500 metres of the Paterangi ''pā'' without detection and arriving in Te Awamutu at dawn. They advanced to the village of Rangiaowhia, where they attacked about 100 mostly elderly men, and about 100 women and children. Most terrified villagers fled, a few shot at the troops, some sheltered in the churches, at least seven were burnt to death in their houses and at least one attempted to surrender, but was murdered by troops ignoring their orders. Women were raped and killed in front of children. About a dozen houses were burned down. The British claimed they killed 12 Māori, including two chiefs, and took 30 prisoners. Their own losses totaled five, including several officers. Some unofficial estimates suggest there were more than 100 Māori deaths. As the village was largely occupied by women, children and older men, the deaths have been regarded as murder, rather than an act of war.
When Cameron's forces returned to Te Awamutu, the men of Rangiaowhia abandoned Paterangi, Pikopiko, and Rangiatea ''pā'' to defend their families and began rapidly digging a new trench on the crest of a ridge at Hairini, cutting the route between Te Awamutu and Rangiaowhia. The trench, fortified with a parapet and stakes, ended in swamp at one end and thick bush at the other. A thousand of Cameron's men, supported by three Armstrong guns, advanced on an estimated 100 Māori manning the frontline on the morning of 22 February. With the Armstrong guns firing over their heads, the infantry, cavalry and Forest Rangers moved towards the defensive line before finally charging with bayonets, revolvers and sabres, driving out the Māori. The British forces pursued the Kingites to Rangiaowhia, where they looted the village and later built a redoubt. Belich claims the so-called "Battle of Hairini" was simply a delaying tactic by the Māori, allowing them to move as many supplies as they could from Rangiaowhia and the Paterangi line. He says the Kingites, by abandoning the Paterangi line, managed to save their army which otherwise would have been destroyed in an all-out pitched battle; Cameron's decision to outflank the Paterangi line, meanwhile, was described as a "brilliant" strategy that forced his enemy out of one of its richest economic centres with minimal British losses, becoming the greatest British victory of the Waikato invasion. For Kingitanga supporters, who after the Rangiriri battle had been urged to fight in a "civilised" manner by the British, and had moved their families away from their fortifications to an undefended, open village, the assault on Rangiaowhia was an almost "incomprehensible act of savagery".
The role of Bishop Selwyn in the Rangiaowhia attack is unclear. He came with the invading forces, but also helped with Māori burials. The wife and two daughters of Kereopa Te Rau
Kereopa Te Rau (? – 5 January 1872) was a leader of Pai Mārire (Hauhau), a Māori religion. He played a key role in the Volkner Incident and was subsequently hanged for his part in it.
Early life
Little is known of Kereopa's early life but h ...
were killed in the attack, and his sister was killed in defence of the Hairini line a few days later. Colonel Marmaduke Nixon, who had led the Rangiaowhia cavalry charge, was mortally wounded. His remains are buried at the Nixon memorial in Ōtāhuhu
Ōtāhuhu is a suburb of Auckland, New Zealand – to the southeast of the CBD, on a narrow isthmus between an arm of the Manukau Harbour to the west and the Tamaki River estuary to the east. The isthmus is the narrowest connection between the ...
, Auckland. There were no memorials to the victims of Rangiaowhia until the 150th anniversary was commemorated in 2014 with the unveiling of a plaque.
Ōrākau
 Following the fall of the Paterangi line, Wiremu Tamihana, leading one of the two major Kingite divisions, retreated east to Maungatautari to block a British advance up the Waikato River into Ngati Raukawa territory and
Following the fall of the Paterangi line, Wiremu Tamihana, leading one of the two major Kingite divisions, retreated east to Maungatautari to block a British advance up the Waikato River into Ngati Raukawa territory and Matamata
Matamata () is a town in Waikato, New Zealand. It is located near the base of the Kaimai Ranges, and is a thriving farming area known for Thoroughbred horse breeding and training pursuits. It is part of the Matamata-Piako District, which takes ...
beyond. Cameron remained at Rangiaowhia, preparing to pursue him. Rewi Maniapoto, with the other main division, moved south into the Hangitiki Valley to defend Ngati Maniapoto bases. Ngati Maniapoto fighters and their allies remained determined to continue the war, but were divided over their strategy: whether to guard the hinterland with large defensive systems on the fringes, or to challenge the nearby occupying forces with a new ''pā''. Rewi deferred a decision until he could consult with Tamihana, the kingmaker, and set out with a small group to Tamihana's stronghold near present-day Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge bec ...
on the upper Waikato. On the way he encountered a group of about 140 of the dispersed Paterangi army, mainly warriors from distant Tūhoe and Ngati Raukawa ''iwi''. The Tūhoe chiefs urged Rewi to build a ''pā'' at the agricultural village of Ōrākau, near Kihikihi
Kihikihi, a small town located in the Waikato region of the North Island of New Zealand, serves as a satellite community of Te Awamutu, five kilometres to the north, and lies 35 kilometres south of Hamilton. The 2018 New Zealand census recorded ...
, to challenge the troops, explaining that their guns and ammunition had been carried a long distance and were "too heavy to carry all this way for nothing". Although he strongly opposed the plan, convinced it would result in their defeat, Rewi relented—possibly in return for the loyalty they had shown in crossing the North Island to join the fight for his territory—and accompanied them back to Ōrākau, arriving about 28 March.
For Rewi, a skilled strategist and warrior, the major concerns about Ōrākau were that it had no immediate water supply and, sited on a low hill, overlooked by the nearby "California" ridge, 850m to the southwest, could also be easily encircled. The land immediately to the south of the pa was a series of low undulating hillocks leading to swamp. For two days the villagers, as well as Rewi's forces and the new reinforcements, labored in shifts to strengthen the defences of the ''pā'', located on a slight rise of land in the midst of peach groves. Measuring about 30 metres by 12 metres, the ''pā'' was enclosed within a rectangular redoubt and contained interior bunkers, trenches, firing apertures. The main parapet was just 1.2 metres high, the outer trench a metre deep and the entire system was surrounded by a post and three-rail fence. The ''pā'' was defended by between 200 and 250 warriors—mainly Tūhoe and Ngati Raukawa—drawn from at least nine tribes, as well as about 50 women and children.
Early on 30 March two surveyors working at Kihikihi observed through a telescope construction of entrenchments at the Ōrākau pā and immediately passed the information to Brigadier General G. J. Carey, who had been left in charge of the British forces. Carey, keen to surprise the Kingites, immediately began organising an expedition and at midnight the first of three separate columns, comprising members of the 40th, 65th and 18th Royal Irish Regiments, as well as Forest Rangers and Waikato Militia, set out for Ōrākau with two Armstrong six-pounders, arriving before daybreak. The total force for the mission was 1120 men. The two cannons were set up on a small plateau 350m to the west and about the same height above the ''pā''. They were shooting across the front of the 40th Regiment who were situated 250 m south of the ''pā'' behind a small hill.
31 March – 1 April, days one and two
Early on 31 March the first attack was made on Ōrākau, whose parapets and exterior fence was still incomplete. The Ōrākau garrison spotted the attacking force to their west just minutes before the bugle was sounded to charge and warriors were ordered by Rewi into the outer trenches. The Kingites held their fire until the attackers were within 50 metres, then fired in two volleys, halting the advance. Two more waves of attack were similarly repulsed, with several casualties, including officers. Realising the strength of Ōrākau, Carey decided to encircle the ''pā'' and began shelling it from about 350 metres, though the design and construction methods of the bunkers neutralised the force of the bombardment. He then ordered a start on a shallowsap
Sap is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a separa ...
that zig-zagged towards its western face from a distance of about 120 metres. A party of Māori reinforcements appeared about 2 km to the east, but retreated, unable to break through the British lines. Sporadic shooting continued through the night, with the besieged occupants of Ōrākau chanting and singing.
By dawn the second day—with fog so thick the combatants could not see one another—the Ōrākau garrison realised they had exhausted their water supplies and most of their ammunition. Ngati Maniapoto chief Winitana Tupotahi suggested at a ''runanga'', or council of chiefs, that they abandon the ''pā'', but Rewi rejected the proposal. At midday many attempted to break out of the ''pā'' through the cordon at the east, but were driven back twice, suffering the loss of one of their chiefs. One Kingite told Cowan: "We were in better spirits after our fight in the open; nevertheless we realized that our position was hopeless, short of food and water, short of lead, and surrounded by soldiers many times outnumbering our garrison, and with big guns throwing shells into our defences." Further British reinforcements arrived, including a second company of Forest Rangers, taking the British strength to almost 1500. Shelling continued as the sap approached the ''pā'', its progress slowed by accurate fire from the Kingites.
That night, Tupotahi suggested they make a breakout under cover of dark. Rewi supported the plan, but the ''runanga'' decided they should stay and fight. With ammunition now running very short, the Kingites—so parched they could not swallow their remaining food—began firing peach stones, 5 cm-long sections of apple tree branches and pieces of metal.
2 April: day three
 Another ''runanga'' was held before dawn on 2 April and again Tupotahi urged them to break out. Though many of the chiefs remained steadfast in their refusal to retreat, Rewi insisted the effect of the water shortage was now so severe they had to break out, but urged they go out fighting. The plan was aborted when dawn broke and the fog lifted, removing their cover. Through the morning the British sap advanced close enough to the outer trenches of Ōrākau for hand-grenades to be thrown over the ramparts. At noon Cameron arrived with more men, bringing the besieging imperial and colonial force to 1800. One of the Armstrong guns was moved to the head of the sap and fired at the
Another ''runanga'' was held before dawn on 2 April and again Tupotahi urged them to break out. Though many of the chiefs remained steadfast in their refusal to retreat, Rewi insisted the effect of the water shortage was now so severe they had to break out, but urged they go out fighting. The plan was aborted when dawn broke and the fog lifted, removing their cover. Through the morning the British sap advanced close enough to the outer trenches of Ōrākau for hand-grenades to be thrown over the ramparts. At noon Cameron arrived with more men, bringing the besieging imperial and colonial force to 1800. One of the Armstrong guns was moved to the head of the sap and fired at the outwork
An outwork is a minor fortification built or established outside the principal fortification limits, detached or semidetached. Outworks such as ravelins, lunettes (demilunes), flèches and caponiers to shield bastions and fortification curtains ...
of the ''pā'' about 30 metres away, breaching the wall. Under the combination of shells, hand grenades and rifle fire, Māori casualties began to climb rapidly.
Soon after arriving, Cameron, impressed by the courage of the garrison, decided to give them the opportunity to surrender. Two interpreters were sent to the head of the sap with a white flag and Major William Mair called out the offer in Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
, which was passed to Rewi, within the ''pā''. Although there are several versions of Rewi's reply, he is reputed to have declared through his messenger, "''Ka whawhai tonu ahau ki a koe, ake, ake''" ("I shall fight you forever, and ever, and ever") When a shot was fired at Mair as he withdrew, grazing his shoulder, the British forces responded with a heavier hail of grenades, artillery and gunfire. The Ōrākau garrison repulsed two more attempts by the Waikato militia to rush the north-west outworks, but at 4:00 pm the chiefs, realising the end was near, decided to break out. Placing women and children in the middle of the group and their best warriors in front, the Māori broke through the earthworks at the south-east corner of the ''pā'' and ran downhill without opposition 200 metres towards a ridge to the south, behind which the some men of the 40th were sheltering. They then dropped down a sloping 10-metre bank, surprising members of the 40th Regiment, who formed the south eastern edge of the cordon before running for cover in a nearby swamp. The group, many of them holding empty shotguns or tomahawks, was pursued by sword-bearing cavalry and hundreds of soldiers who fired on and bayoneted the fleeing Māori; Forest Rangers kept up the chase until dusk. Back at Ōrākau, meanwhile, soldiers stormed the ''pā'' as the garrison fled, bayoneting and shooting many of the wounded, including women and children. One of the women was Hine-i-turama Ngatiki.
Sixteen of the British forces died in the three-day battle and 53 were wounded, some of them mortally; while estimates of Māori fatalities range from 80 to 160, with half of the casualties coming from the Urewera contingent. Another 26 wounded were taken prisoner. The bodies of the Māori were buried in mass graves in the trenches of Ōrākau (just to the north of the road opposite the existing memorial) and beside the nearby swamp to the south. Rewi escaped through the swamp, unharmed, escorted by a 12-man bodyguard.
The Māori saw Ōrākau as a defeat, but both Cameron and Grey were angered by the failure of the 40th Regiment to halt the Ōrākau breakout and kill Rewi, which deprived them of the crushing victory over the Kingites they desperately sought.
The general site of the battle is today marked by a memorial on Arapuni Road, 4 km east of Kihikihi, with the road running through the middle of what were the defences. The site of the ''pā'' is on private farmland and no traces of it are now visible. Plans have been proposed to commemorate the 150th anniversary of the battle in 2014, with a call made for a new memorial.
Commissariat
Belich has described the Waikato campaign as one of the best-prepared and best organised ever undertaken by the British Army, proving that many lessons had been learned from the logistical fiasco of the Crimean War. He said the Commissariat Transport Corps (CTC), established in mid-1861, almost two years before the invasion began, was the "vital kernel" because of its efforts in building the southern road and being a separate military supply train. Commissariat sourced much of its food from England and Australia and sent it along with other supplies up to 160 km into the interior via a combination of steamers, barges, bullocks and pack horses. The CTC had found theOtago pack saddle
The Otago pack saddle, later known as the British universal pack saddle, is a rideable pack saddle devised by Harvey Spiller in Otago, New Zealand, in 1863, to prevent ruinous injuries to horses carrying heavy loads. It was improved and ad ...
, devised in the Otago goldfields to prevent injury and ruin to horses carrying heavy loads, to be the best suited to their needs. In a report to the War Office, Commissary General Humphrey Stanley Herbert Jones described the CTC as "the foundation of the whole service". The work of the commissariat helped ensure the sick rate of soldiers never rose above 5 percent—a rate far below that of the Crimean War a decade earlier, when 14 percent of the force was incapacitated.
Aftermath
Ōrākau was the last major battle of Cameron's Waikato campaign. Leaving his captured territory occupied by troops, he resumed his preparations to assault one of the strongest of Tamihana's ''pā'', Te Tiki o te Ihingarangi, about 25 km northeast of Ōrākau near modern-dayLake Karapiro
Lake Karapiro () is an artificial reservoir lake on the Waikato River at Karapiro, south-east of Cambridge in New Zealand's North Island. The lake was formed in 1947 by the damming of the Waikato River to store water for the 96-megawatt Karap ...
. The ''pā'' formed part of a long line of ''pā'' the Kingites called ''aukati'', or boundary. Cameron assessed the ''pā'' as too strong to assault and incapable of outflanking. On 2 April he settled his troops in front of it, and prepared to shell it. After three days the Kingites abandoned the ''pā'', but Cameron decided further effort in the region would be fruitless and withdrew, switching his focus to Tauranga
Tauranga () is a coastal city in the Bay of Plenty region and the fifth most populous city of New Zealand, with an urban population of , or roughly 3% of the national population. It was settled by Māori late in the 13th century, colonised by ...
. Land behind the ''aukati'' remained native territory, with Europeans warned they crossed it under threat of death. The area subsequently came to be known as the King Country
The King Country (Māori: ''Te Rohe Pōtae'' or ''Rohe Pōtae o Maniapoto'') is a region of the western North Island of New Zealand. It extends approximately from the Kawhia Harbour and the town of Otorohanga in the north to the upper reaches of ...
.
In mid-1863 the New Zealand government began planning legislation designed to punish armed Māori resistance and aggression by widespread confiscation of their land, which would be given to colonial settlers. The New Zealand Settlements Act was passed in December 1863 and in 1865 Governor Grey confiscated more than 480,000 hectares of land from the Waikato–Tainui ''iwi'' (tribe) in the Waikato as punishment for their earlier "rebellion".
Proclamations under the act were issued on 30 January 1865 for the seizure of the East Wairoa and West Pukekohe blocks for settlement and colonisation, followed by the Central Waikato district and the Mangere, Pukaki, Ihumata and Kerikeri blocks (16 May 1865). As the occupants were evicted from their land, their belongings were looted by colonial forces and neighbouring settlers, with houses ransacked, cattle seized and horses transported for sale in Auckland.
The war and confiscation of land caused heavy economic, social and cultural damage to Waikato-Tainui. King Tāwhiao
Tāwhiao (Tūkāroto Matutaera Pōtatau Te Wherowhero Tāwhiao; c. 1822 – 26 August 1894) was leader of the Waikato tribes, the second Māori King, and a religious figure. He was a member of the Ngati Mahuta (Hapū) of Waikato.
Biography
T ...
and his people were forced to retreat into the heartland of Ngāti Maniapoto
Ngāti Maniapoto is an iwi (tribe) based in the Waikato-Waitomo region of New Zealand's North Island. It is part of the Tainui confederation, the members of which trace their whakapapa (genealogy) back to people who arrived in New Zealand on the ...
. The Maniapoto, by contrast, had been more zealous for war than the Waikato, yet suffered no loss of land because its territory was too remote to be of use to white settlers. The 1927 Royal Commission on Confiscated Land, chaired by senior supreme court judge Sir William Sim, concluded that although the government restored a quarter of the 1,202,172 acres (486,500 hectares) originally seized and paid almost £23,000 compensation, the Waikato confiscations had been "excessive". The Waitangi Tribunal
The Waitangi Tribunal (Māori: ''Te Rōpū Whakamana i te Tiriti o Waitangi'') is a New Zealand permanent commission of inquiry established under the Treaty of Waitangi Act 1975. It is charged with investigating and making recommendations on cla ...
in 1985 declared the Tainui people of the Waikato had never rebelled, but had been forced into a defensive war.
In the early 1990s Tainui opted to bypass the Waitangi Tribunal and concluded a treaty claims settlement with the Crown through direct negotiation. In May 1995 the Crown signed a deed of settlement with Waikato–Tainui that included cash and land valued at $170 million. The settlement included an admission by the Crown that it had "unjustly confiscated" the land. It formally and publicly apologised to Waikato–Tainui and the Kingitanga for unjustly invading Waikato–Tainui lands, for sending imperial forces across the Mangataawhiri, and for the loss of life and the devastation of property that ensued. The Crown expressed profound regret and apologised unreservedly for the invasion and the crippling effects it had on the welfare of the Waikato-Tainui people./ref> Queen
Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
affirmed the apology of the Crown by signing the Waikato Raupatu Claims Settlement Act 1995
The Waikato Raupatu Claims Settlement Act 1995 is an act of the New Zealand Parliament passed into law in 1995. It was the first act implementing a major historical Treaty of Waitangi settlement since the Treaty of Waitangi Act 1975 was amended ...
in the presences of the head of the Kingitanga, Māori Queen Dame
''Dame'' is an honorific title and the feminine form of address for the honour of damehood in many Christian chivalric orders, as well as the Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom, British honours system and those of several oth ...
Te Atairangikaahu
Dame Te Atairangikaahu (23 July 1931 – 15 August 2006) was the Māori queen for 40 years, the longest reign of any Māori monarch. Her full name and title was Te Arikinui Dame Te Atairangikaahu. Her title Te Arikinui (meaning ''Paramount C ...
. As a result of this settlement the Crown agreed to return as much land as possible to Waikato and to pay compensation, and said that it sought on behalf of all New Zealanders to atone for these acknowledged injustices, and to begin the process of healing and to enter a new age of co-operation with the Kingitanga and Waikato.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * *External links
War in the Waikato
(NZHistory) {{DEFAULTSORT:Invasion Of Waikato Conflicts in 1863 Conflicts in 1864 New Zealand Wars 1863 in New Zealand 1864 in New Zealand History of Waikato